- Information
- iGambling
- Blask
- prev
- next
Gambling regulation
-
Online casino:Regulated
-
Online sports betting:Regulated
-
Gambling in detail:
Population
- Population: 186988000 people.
- Official Language: English
- HDI: 0,548
- Salary: $160
- Poverty rate: 90.8%
- Gini: 35.1%
- The believing population: 83%
- Main religion: Christianity (49.3%)
- Second religion: Islam (48.8%)
Harmful habits
- Alcohol: 4.5 litres/year
- Smoking: 3.7%
Internet
- Internet users: 63.8%
- Mobile Internet: 88.7%
- Landline Internet: 10.6%
- Internet speed: 18.9 Mbps
- Country Top Level Domain: .NG
General information about the country
-
Country name:Nigeria
-
Code (2-digit):NG
-
Continent:Africa
-
Country level:Tier 3
-
Capital:Abuja
-
Country area:923768 sq km.
-
Telephone code:234
-
Currency (code):Naira (NGN)
Geographical features of the country
Administrative division into regions
Federal Capital Territory: Abuja.
State (33): Abia, Adamawa, Akwa Ibom, Anambra, Bauchi, Benue, Borno, Gombe, Delta, Zamfara, Imo, Yobe, Kaduna, Kano, Katsina, Kwara, Kogi, Cross River, Lagos, Nasarawa, Niger, Ogun, Oyo, Ondo, Osun, Plateau, Rivers, Sokoto, Taraba, Ebonyi, Edo, Ekiti, Enugu, Zamfara.
Features of the country
The modern territory of the country was partially or wholly occupied by the states of Bornu, Oyo, Edo, Songhai, British Empire (now UK), Dahomey, Sokoto.
Nigeria has access to the following lakes: Chad, Lagos, Lekki.
The following rivers flow through the territory: Niger, Benue, Kamadugu-Yobe, Sokoto, Kaduna.
Mountains on the territory of the country: Vogel, Sara Peak.
Gambling regulation
-
Online casinos:Regulated
-
Online sports betting:Regulated
Read more about regulation
The gaming industry is overseen by the National Lottery Regulatory Commission (NLRC), which sets the regulatory framework for the entire country, and by state-level regulators who enforce rules for gambling at the local level.
Legal forms of gambling include betting, lotteries, racing and land-based casinos. There are currently no regulations for online gambling in Nigeria.
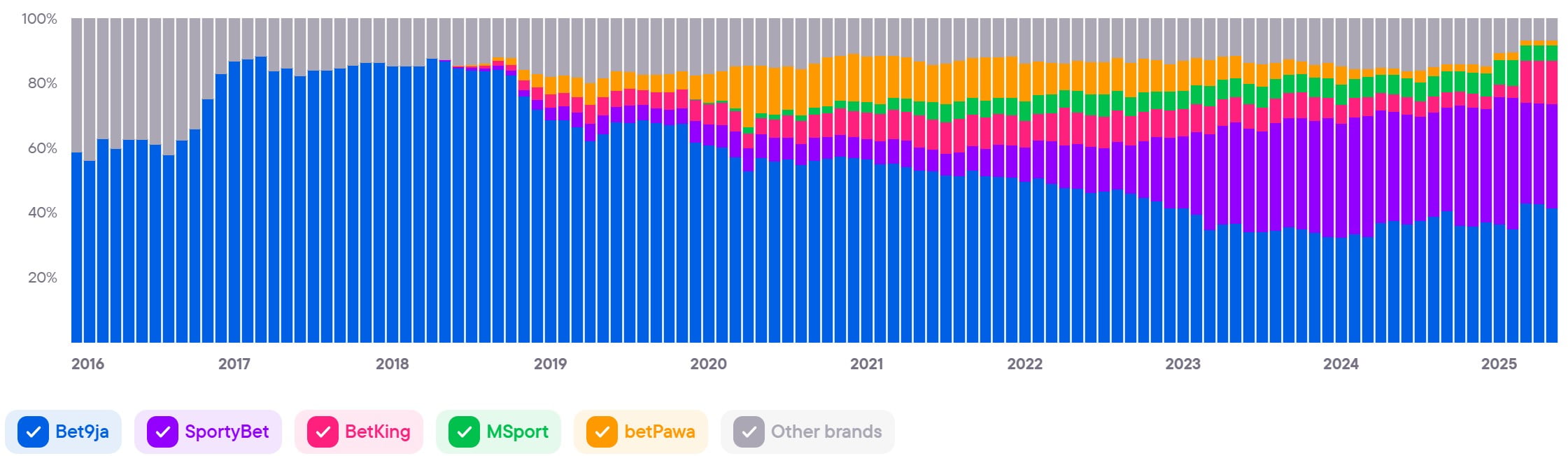
Top brands in the country
Ranking of iGaming brands as of September 2024 (market share)
- Bet9ja (40.12%)
- SportyBet (34.04%)
- MSport (6.4%)
- BetKing (5.3%)
- Betshop (5.04%)
- 1xBet (1.53%)
- Betano (1.27%)
- iLOT Bet (1.14%)
- Bangbet (0.73%)
- Merrybet (0.7%)
- AccessBET (0.55%)
- BC Game (0.46%)
- betBonanza (0.4%)
- NairaBet (0.32%)
- 22bet (0.29%)
- PariPesa (0.26%)
- Sportsbet (0.21%)
- Bet365 (0.2%)
- LiveScoreBet (0.17%)
- Stake (0.1%)
Top payment systems
Payment Methods (November 2024)
- GTPay
- Verve
- Kuda Bank
- PalmPay
- Opay
- Jumia
Cryptocurrency is worth mentioning separately. Crypto betting is growing in popularity in the region, however, crypto exchanges are actively blocked in order to stabilise the naira (national currency).
Gambling work files
Online Gambling in the country
Features of betting and punters
When we talk about Betting, over 76% of all betting is on Football, where the most recognisable and popular league is the APL.
Despite the highest number of young bettors under 30 and increasing digitalisation, more than 60% of all betting in the African region still takes place at offline outlets.
This shows one thing: the African market is about diversification and playing for the long haul, not quick profits.
If you are planning to enter the African market, here is what you need to be prepared for:
- Focus needs to be on outdated technology and devices.
- High risk of website and payment processor failures.
- The average spend for bettors is $5 per month. Low stakes, but in huge volumes
- The average age of an African resident is 20 years old. This should be taken into account in all aspects of operation.
Mentality
The republic is home to about 400 African tribes. 80% of Nigerians are represented by the ten most influential tribes. The official language is English, among local languages there are Hausa, Ibo (Igbo), Yoruba.
Here they believe in the cult of ancestors, witchcraft, black and white magic. Respect for elders is a fundamental principle in the country. Not only those who are older, but also those who, for example, have education, are considered elders.
Most Nigerians tend to be idle. Therefore, their free time is spent on sports (both playing and watching various sporting events in sports bars common in the country) and gambling.
Forecasts
- At the moment, there is a clear dominance of online betting compared to online casinos. However, the slots part is gaining momentum every year and IGB predicts that Nigeria could become the largest slots market in Africa
- GGR online casino forecast for 2025: around 300-350 million USD
- Meanwhile, according to iGaming Research, revenue from the entire gambling market is projected to be around 700 million USD in 2025.
Risks
- Nigeria is far from having the best internet. Yes, the coverage is getting better every year, but it is still a long way from the level of the top countries in the iGaming industry. This can have a negative impact on players' session duration and, as a consequence, ARPU.
- Orientation to mobile devices. The majority (about 85%) of players place bets from mobile devices.
- Low ARPU. On a daily basis, Nigerians place about 18 million bets. However, the bet size is usually minimal, as is the deposit size of about $2.
- Local licence. Nigeria is far from having the strictest regulation, but having a local licence gives players more confidence in the project.
The iGaming market environment
In October 2024, the Nigerian government proposed a 5% excise tax on any telecoms and gambling related transactions. The bill is expected to come into effect in 2025 if approved by the National Assembly.
The initiative is prompted by the economic hardship and high unemployment rate facing the country. By the way, against this backdrop, Nigerians are actively participating in iGaming, expecting to win large sums of money quickly.
In addition to this, gambling operators have been instructed to set up separate wallets for customer winnings to ensure that players have immediate access to their funds. New fees for gambling licences are also being introduced: the cost of a licence for casinos is $59k and for bookmakers $44k.
It is known that in Nigeria more than 60 million people are involved in betting (population is over 230 million), with 9% of them betting every day. Currently, the industry brings in between $308m and $370m annually.
Lagos State (the largest city in Nigeria) accounts for a significant part of this revenue: in 2023 alone it totalled $243 million. It is predicted that by 2025 the GGR of the iGaming market in Nigeria will reach $717.2 million.
Gambling affiliate programs with local licence
Gambling affiliate programmes that accept traffic from this country
- Blask data from: 06/03/2025
- Population: 236,745,000 people.
- Population growth rate: +2.52% per year.
- Internet users: 115,500,000 people.
-
Urbanization:
Urbanization — 54.3%
-
Languages in the country:
English (official)
Hausa
Yoruba
-
Age structure:
0-14 — 40.4%
15-64 — 56.2%
65+ — 3.4% -
Median age:
Total — 19.3
Male — 19.1
Female — 19.6 -
Literacy:
Total — 62%
Male — 71.3%
Female — 52.7%
-
Real GDP:
2021 — $1.2 trillion
2022 — $1.239 trillion
2023 — $1.275 trillion -
Real GDP growth:
2021 — 3.65%
2022 — 3.25%
2023 — 2.86% -
Real GDP per capita:
2021 — $5,600
2022 — $5,700
2023 — $5,700
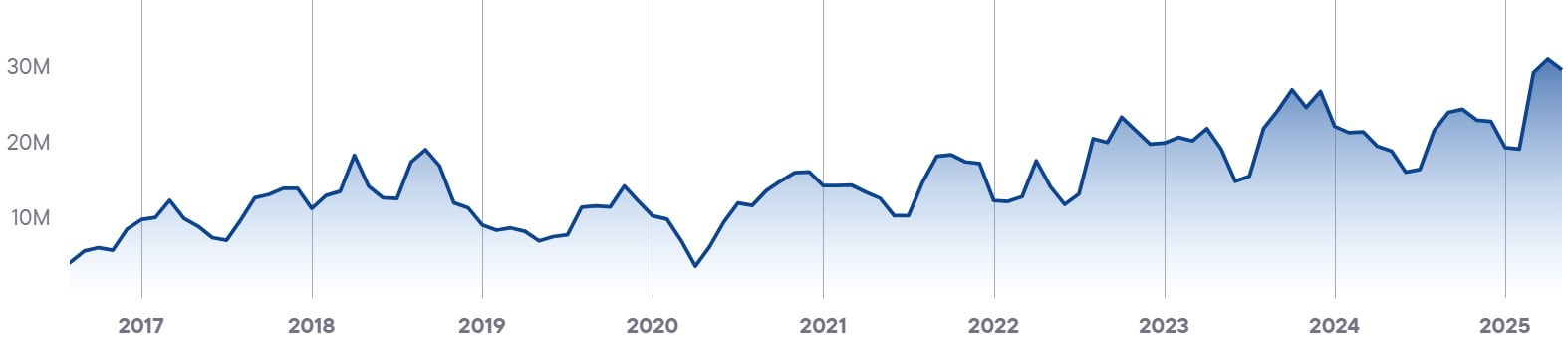
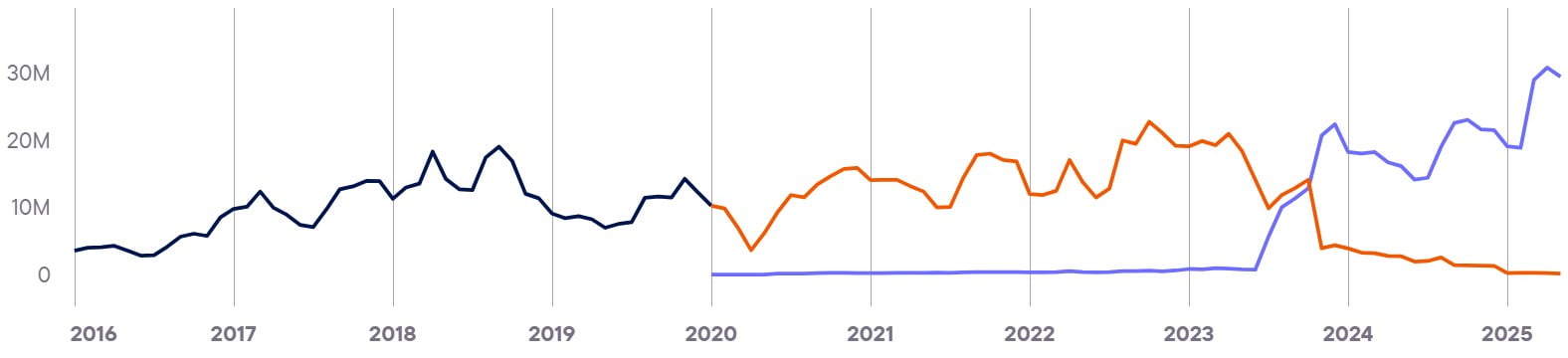
Blask Index
Top brands in the country
| Brands | BAP* |
|---|---|
| Bet9ja | 41,6 |
| SportyBet | 32,4 |
| BetKing | 13,4 |
| MSport | 4,8 |
| betPawa | 1,4 |
- The data for this section was provided by the analytical service Blask.com. Currently, the service's database contains information on 62 countries and more than 2,500 brands. You can view all available countries with Blask statistics at this link.
- Share
- prev
- next